Troubleshooting Internet ConnectivityUpdated 20 days ago
Having trouble connecting your PC to Wi‑Fi? We are here to help! This guide walks you through quick steps to get back online. We start with the basics and move toward more advanced checks if the issues continue.
Please note: META PCs can only troubleshoot your computer and its internal hardware. If the problem is caused by outside equipment—such as your router, modem, or Wi‑Fi hotspot—contact your Internet Service Provider (ISP). META PCs does not provide troubleshooting for external network hardware.
MY WIFI DOES NOT WORK AT ALL
You don’t see a Wi‑Fi icon, can’t select a network, or Windows shows “No Wi‑Fi networks found.”
CHECK WIFI SETTINGS
In Windows, go to Settings → Network & Internet → Wi‑Fi.
Make sure Wi‑Fi is "On" and Airplane mode is "Off".
Select your network, click Connect, and enter the password.
When prompted, choose Private network for home networks (recommended).
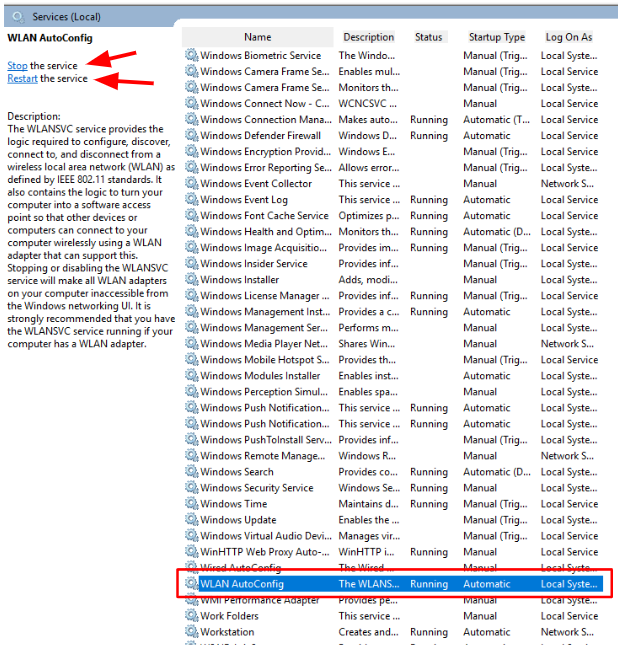
CHECK THE WLAN SERVICE
Press Windows key, type "services.msc" and press Enter.
Find "WLAN AutoConfig".
Make sure the Status is "Running" and Startup Type is "Automatic"
If it isn’t running, right‑click it, and select "Start". If it’s running, right‑click it, and select "Restart".
POWER CYCLE KEY DEVICES
If the service is running and Wi‑Fi is still missing or won’t connect:
Power cycle your PC: Shut down, wait 15 seconds, then turn it back on.
Power cycle your modem/router: Unplug the power for 30 seconds. Plug in the modem first; wait until it’s fully online. Then, power the router on. Wait 2–3 minutes for Wi‑Fi toinitialize and broadcast.
TRY A WIRED CONNECTION
Plug an Ethernet cable from your PC to the router.
If the internet works on Ethernet, the issue is likely wireless drivers, antenna, or signal. Continue below.
UNINSTALL AND REINSTALL NETWORK DRIVERS
Use Device Manager to reinstall the Wi‑Fi adapter, then update drivers.
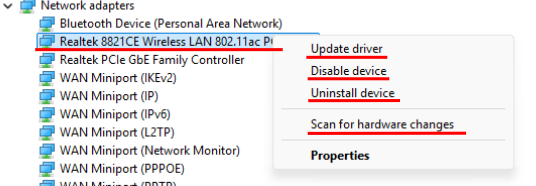
A. Check Device Manager
Right click on the Windows Icon in your task bar and select Device Manager.
Expand Network adapters. Look for your Wireless/Wi‑Fi adapter.
Also check Other devices for any item with a yellow warning icon.
Right‑click your Wi‑Fi adapter → Uninstall device → check Attempt to remove the driver → Uninstall.
In Device Manager, click Action → Scan for hardware changes (or reboot) to reload the baseline driver.
B. If Ethernet Works (Recommended path)
Connect via Ethernet.
Use your motherboard’s tool to install the latest network drivers:
Install all Wireless/WLAN and Bluetooth drivers offered. Reboot.
C. If Ethernet Does Not Work (Offline USB install)
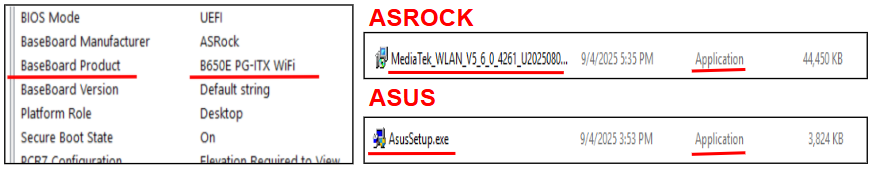
On your META PC, press Windows key and type System Information. Open it.
Note the Baseboard Product (your motherboard model). Take a photo or write it down.
On another PC with internet, search for your motherboard model (using the information gathered prior) on the manufacturer’s site.
Go to Support → Drivers/Downloads and download Wireless/WLAN/Wi‑Fi drivers.
Copy the .zip to a USB drive. Move it to your META PC.
Right‑click the zip → Extract All… → open the extracted folder.
Run the installer (for ASUS, this is typically ASUSSETUP.exe; ASRock packages may provide a single .exe file amongst the other options). Follow the prompts and reboot.
UPDATE YOUR BIOS
If drivers don’t restore Wi‑Fi, update to the latest BIOS for your motherboard.
RESET YOUR OS (LAST RESORT)
If Wi‑Fi still won’t work, reinstall Windows.
Or use Windows Reset: Settings → System → Recovery → Reset this PC. Choose Keep my files (apps will be removed) or Remove everything (full wipe). Be sure to back up important data before continuing!
MY WIFI WORKS BUT THE SIGNAL IS WEAK OR SPEED IS SLOW
Wi‑Fi connects, but pages are slow, streaming buffers, or you see a one‑bar signal.
CHECK YOUR ANTENNAS
Locate the motherboard I/O on the back of the PC.
Find the two Wi‑Fi antenna posts (often brass screw‑on or black push‑in types).
Attach both antenna leads. Orientation doesn’t matter; so long as they’re firmly seated.
Angle antennas apart (e.g., 45°/135°) and avoid metal obstructions behind the PC.

Reinstall your Motherboard's WiFi Drivers
On your META PC, press the Windows key and type System Information. Open it.
Note the Baseboard Product (your motherboard model). Copy it your clipboard (CTRL + C) and paste it into your browser of choice.
Find the Motherboard Manufacturer's dedicated page for your motherboard
Go to Support → Drivers/Downloads and download Wireless/WLAN/Wi‑Fi drivers.
Right‑click the zip → Extract All… → open the extracted folder.
Run the installer (for ASUS, this is typically AsusSetup.exe; ASRock packages will provide a single '.exe' file amongst the other options). Follow the prompts and reboot.

CHECK YOUR DISTANCE
2.4 GHz travels farther and penetrates walls better, but is slower.
5 GHz is faster with less interference, but has shorter range.
Tips:
If you’re far from the router or have many walls, try the 2.4 GHz network.
If you’re close to the router, use 5 GHz for best speeds.
Reposition the router higher and centered; reduce obstructions.
Consider a Wi‑Fi extender, mesh system, or moving your setup or router so that you are positioned closer to it.
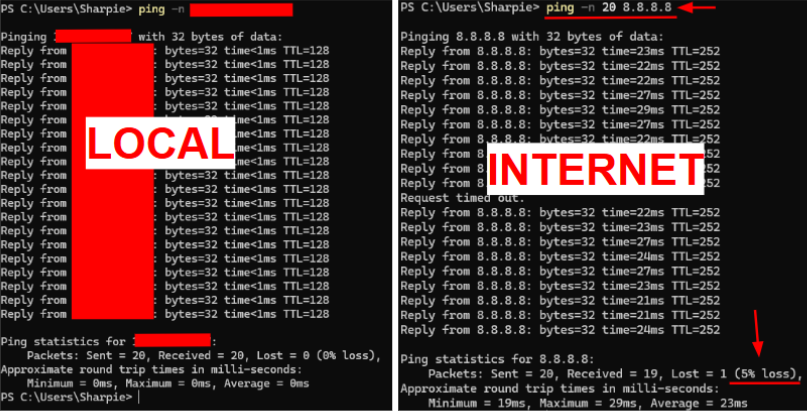
CHECK FOR PACKET LOSS
Press Windows + R, type cmd, press Enter.
Test your router: Paste and run the command "ping -n 20 xxx.xxx.x.x", replacing the "x" with your IP address (you can find that by simply googling "What is my IP?" or by following step 4). 0% loss is ideal.
Test the internet: Paste and run the command "ping -n 20 8.8.8.8". Repeated loss suggests a line or ISP issue. You should see no greater than 5% packet loss.
If local pings are fine but internet pings drop, contact your ISP.
Optional diagnostics: ipconfig /all to verify you have an IP address, gateway, and DNS.