My PC has no display, what can I do?Updated 19 days ago
If you turn on your PC and nothing shows up on the screen, don’t worry — this doesn’t always mean your computer is broken. A no display issue can be caused by many small things, from a loose cable to a simple hardware seating problem.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the most common reasons your PC may not show a display and the steps you can take to fix it. We’ll cover everything from checking your display connections to motherboard debug lights, reseating components, and even trying integrated graphics if your CPU supports it.
By the end, you’ll know how to narrow down the problem and either solve it yourself or be ready to provide clear information if further support is needed.
CHECK YOUR DISPLAY CONNECTIONS
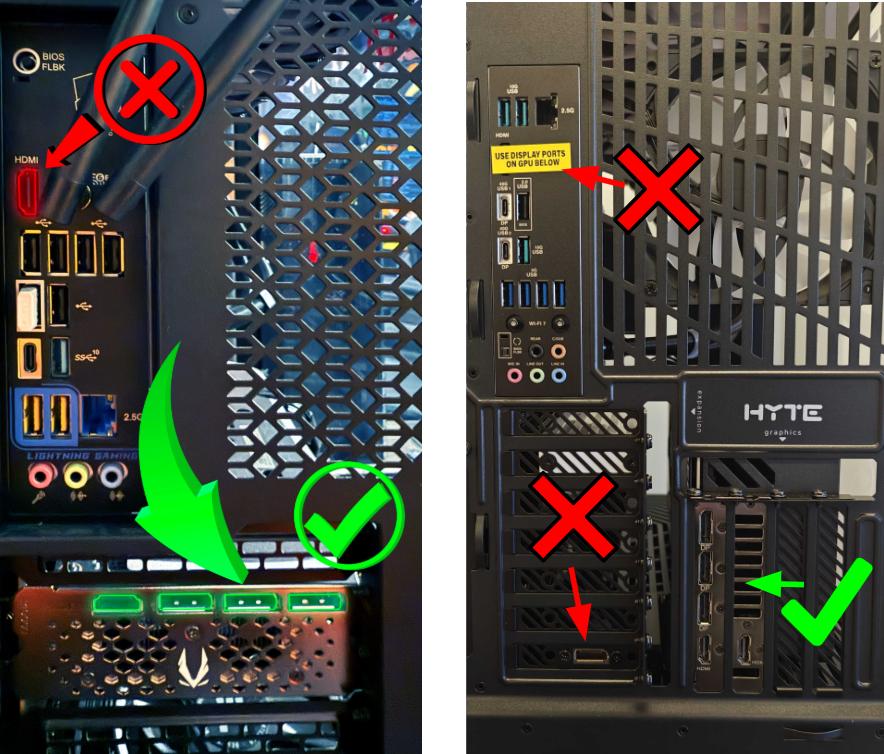
Make sure your monitor cable (HDMI or DisplayPort) is plugged into your graphics card, not the motherboard. The graphics card ports are lower on the back of your PC. The motherboard ports are higher up near USB and audio.
Also, if you have another verified working monitor or cable, test them one at a time. This helps rule out bad cables or displays.
 Examples of horizontal (left) and vertically mounted (right) graphics cards
Examples of horizontal (left) and vertically mounted (right) graphics cards
CHECK YOUR MONITOR CONNECTIONS
Before diving into the PC itself, it’s important to make sure your monitor is set up correctly. A powered-off monitor or the wrong input setting can make it look like your PC isn’t working, even if it’s running fine.
HOW TO CHECK YOUR MONITOR
VERIFY THE MONITOR HAS POWER
Make sure the monitor’s power cable is securely connected.
Look for a power light or logo on the screen when you press the power button.
If there’s no sign of power, try a different power cable or outlet.
CHECK THE VIDEO CABLE
Ensure the HDMI, DisplayPort, or other video cable is firmly connected to both the monitor and your PC.
Try reseating the cable or testing with a known good cable if possible.
CONFIRM THE CORRECT INPUT SOURCE
Most modern monitors have multiple input options (HDMI1, HDMI2, DisplayPort, etc.).
Use the monitor’s on-screen menu (accessible by its buttons or joystick) to cycle through inputs until you see a signal.
TEST WITH ANOTHER DEVICE (OPTIONAL)
If you’re unsure whether the monitor is the problem, try plugging in a laptop or gaming console.
If that also doesn’t display, the issue may be with the monitor itself.
MOTHERBOARD DEBUG LIGHTS
Some motherboards include small diagnostic lights (sometimes called Q-LEDs, EZ Debug LEDs, or Status LEDs) that help you figure out why your system isn’t showing a display. These lights turn on during startup and will stay lit if the system fails at a certain step.
The lights usually follow the same functionality across motherboard brands:
CPU – The processor is not initializing.
DRAM – Memory isn’t being detected or is unstable.
VGA – Graphics card isn’t detected.
BOOT – All core components are recognized and system should be functional
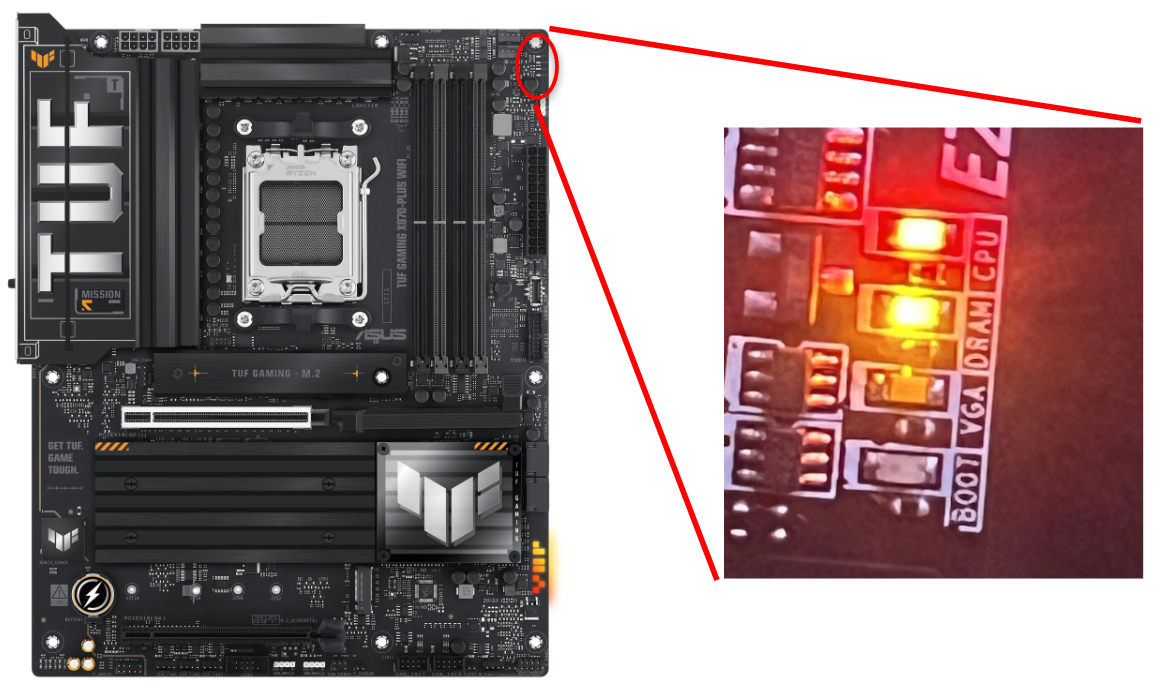 Example of an ASUS motherboard with the DRAM light on, signifying a potential issue with RAM
Example of an ASUS motherboard with the DRAM light on, signifying a potential issue with RAM
POST LIGHT INDICATORS
CPU LIGHT ON – Please contact the META PC Support Team for assistance.
DRAM LIGHT ON – Reseat your RAM, test one DIMM at a time, and try different slots.
VGA LIGHT ON – Reseat your graphics card, confirm power connectors are plugged in, and check your monitor power and video cables are connected.
BOOT LIGHT ON – Your system should be operational. Please check to ensure you are plugging your video connections into the graphics card.
POST CODE DISPLAYS
Some higher-end boards may have a two-digit POST code display (sometimes called “Dr. Debug” or “Q-Code”), which provides a more detailed code you can cross-reference in your motherboard manual as the manual will list what each light or code means.

| SEARCH AND DOWNLOAD MOTHERBOARD MANUALS | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ASROCK | ASUS | GIGABYTE | MSI |
💡Tip: If you need help understanding what troubleshooting steps to take with the code the motherboard is displaying, reach out to the META PC Support Team. We're happy to help!
RESEAT THE RAM
(skip to 1:49)
RESEAT THE GRAPHICS CARD
TRY USING INTEGRATED GRAPHICS
If you are not getting a display through your graphics card, there may be a problem with it. One way to rule this out is to try using integrated graphics, or in other words, remove your graphics card and use your CPU as the video output.
⚠️Please note that not all CPUs have integrated graphics. If your CPU doesn’t support integrated graphics, your motherboard’s video ports will not work.
HOW TO QUICKLY CHECK IF YOUR CPU HAS INTEGRATED GRAPHICS:
- Look up your exact CPU model by referencing the specs of your system on your original META PC order
- Using the links below, go to the processor manufacturer's product search pages and locate your CPU. To make it easier, we have included some example searches below
- If your CPU supports integrated graphics please move on towards the next section
| PROCESSOR SPECIFICATION SEARCH | |
|---|---|
| AMD | INTEL |
AMD EXAMPLE SEARCH
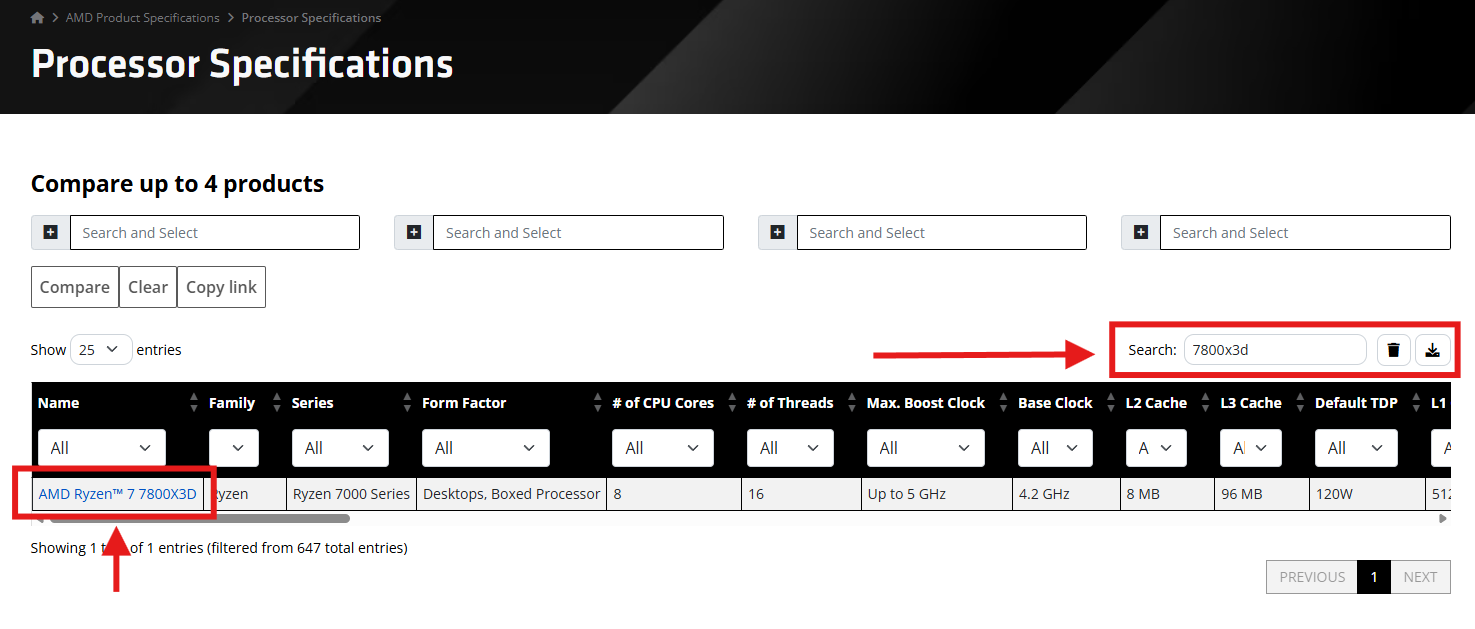 Example of an AMD product search for a Ryzen 7 7800X3D
Example of an AMD product search for a Ryzen 7 7800X3D
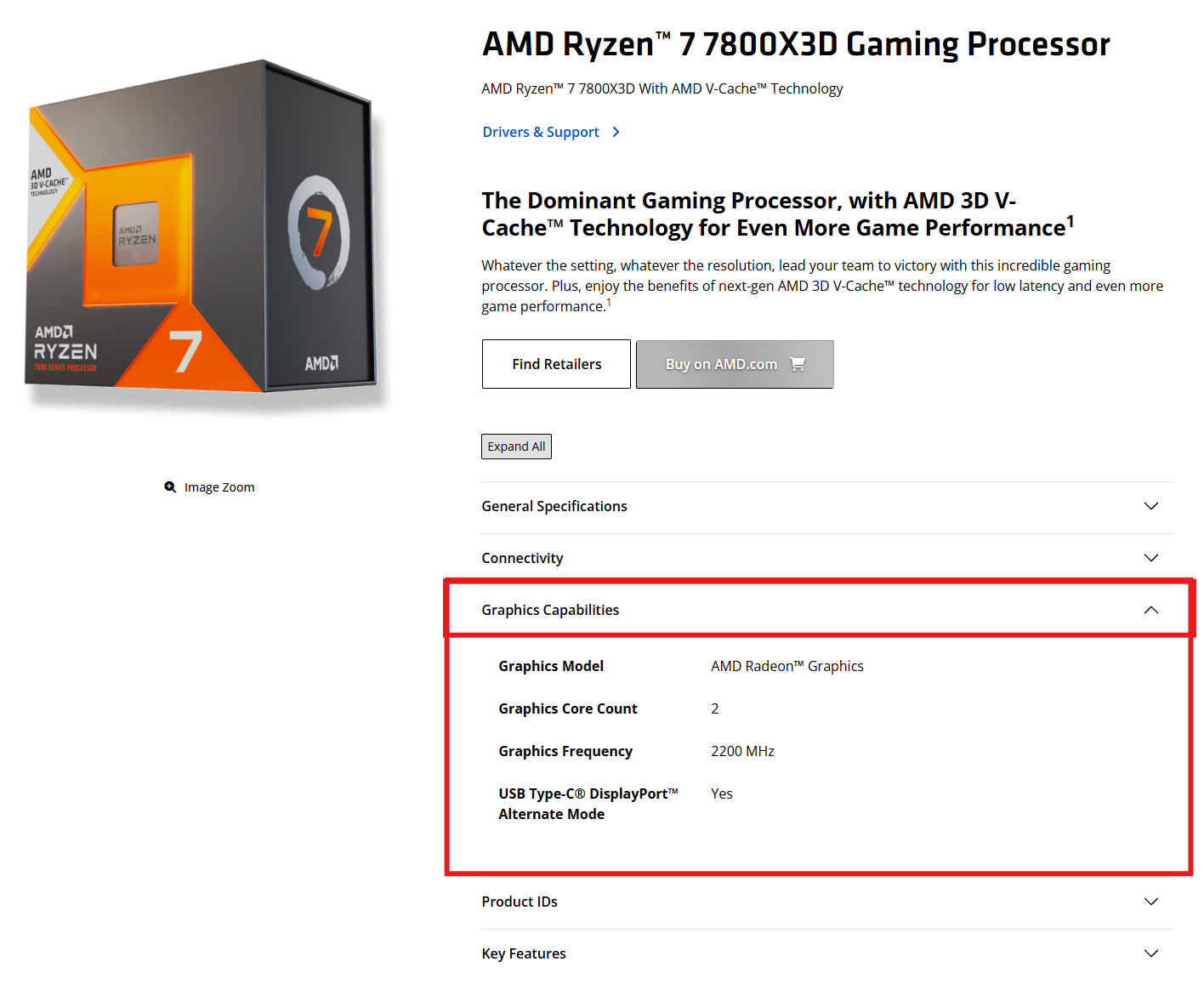 AMD product specification page showing the Ryzen 7 7800X3D does have graphics capabilities
AMD product specification page showing the Ryzen 7 7800X3D does have graphics capabilities
INTEL EXAMPLE SEARCH
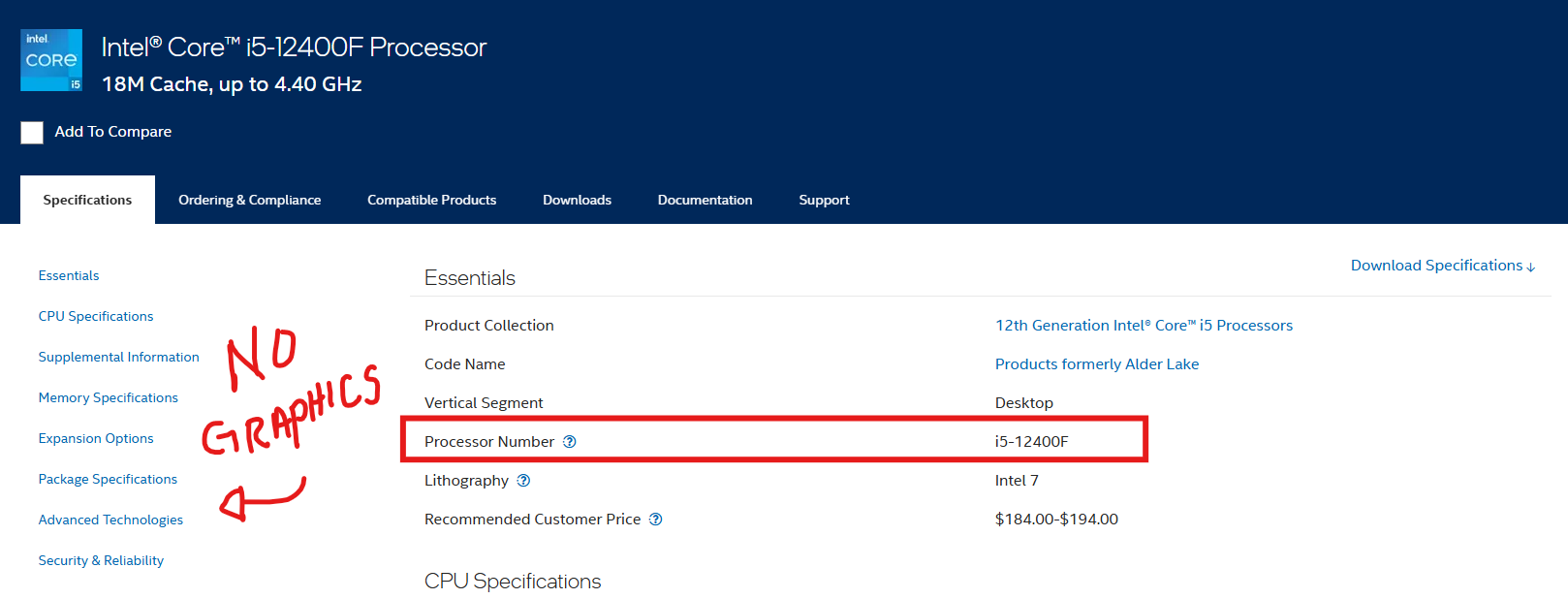 Intel Core i5-12400F with no graphics section on the left (no integrated graphics)
Intel Core i5-12400F with no graphics section on the left (no integrated graphics)
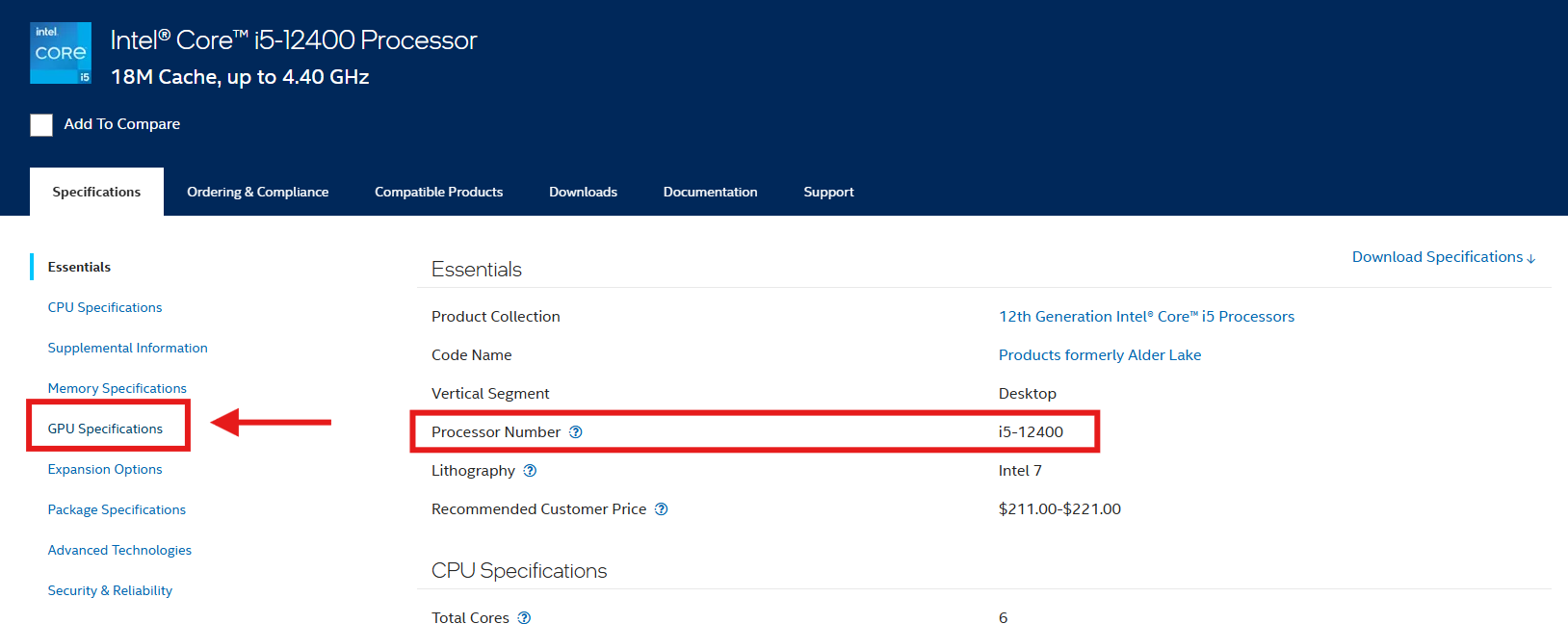 Intel Core i5-12400 with a graphics section on the left (supports integrated graphics)
Intel Core i5-12400 with a graphics section on the left (supports integrated graphics)
MY CPU SUPPORTS INTEGRATED GRAPHICS, NOW WHAT?
REMOVE YOUR GRAPHICS CARD
Power off your PC completely and unplug it from the wall. Carefully remove the graphics card from the PCIe slot. If it helps, here is a video going over how to reseat your graphics card, which covers how to remove a graphics card from a system.
PLUG YOUR MONITOR INTO THE MOTHERBOARD
Use an HDMI or DisplayPort cable to connect your monitor directly to the motherboard’s video output ports. These are usually located above the USB ports on the back of your PC.
POWER ON THE SYSTEM
If the CPU supports integrated graphics, you should see the system power up and give you a display output.
CHECK YOUR RESULTS
- If you get a display → Your graphics card or its connection may be the problem. Reseat the card, check the power connectors, or test with another graphics card.
- If you still get no display → The issue is likely elsewhere (RAM, CPU, motherboard, or monitor setup).
CHECK ALL POWER CONNECTIONS
Your PC won’t display anything if the motherboard or graphics card isn’t getting proper power. Even a loose connector can prevent the system from starting correctly.
HOW TO CHECK MOTHERBOARD POWER
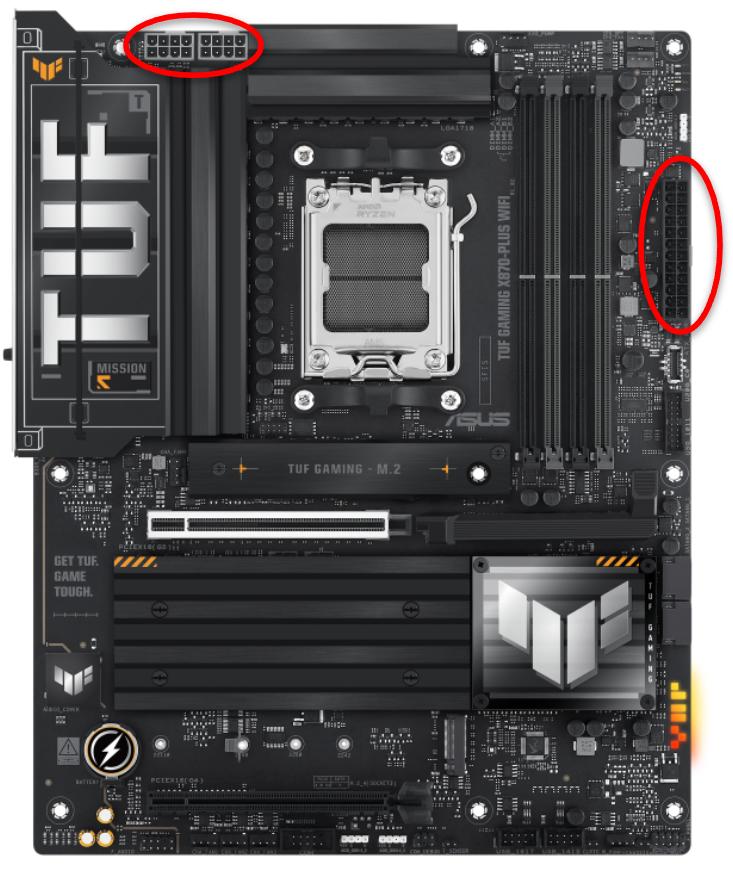
24-PIN ATX CONNECTOR
Locate the large 24-pin cable that plugs into the right side of the motherboard.
Make sure it’s fully seated and latched in place. Sometimes it looks connected but is slightly loose.
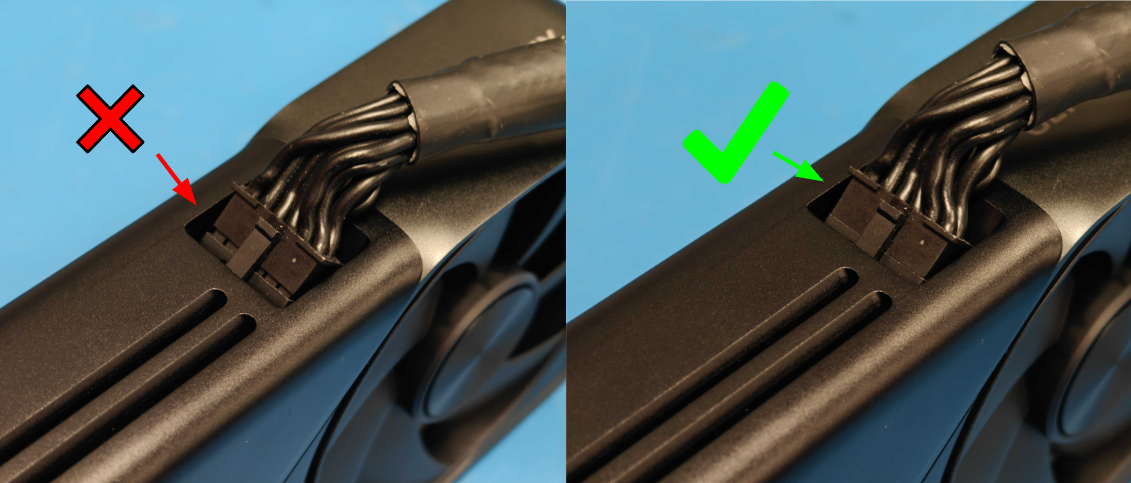
8-PIN (OR 4+4) CPU CONNECTOR
Near the top left of the motherboard, check the 8-pin CPU power connector.
Ensure it’s plugged in fully. Some boards may require both an 8-pin and an additional 4-pin connector for high-end CPUs

HOW TO CHECK GRAPHICS CARD POWER
PCIE POWER CONNECTORS
Many graphics cards require one or more PCIe power cables (6-pin, 8-pin, or a combination).
Check that each connector is plugged in securely and clicked into place.
VISUAL CHECK
The connectors should be straight and flush with the GPU.
A partially connected cable can cause the system to power on but give no display.